- Cuba
-
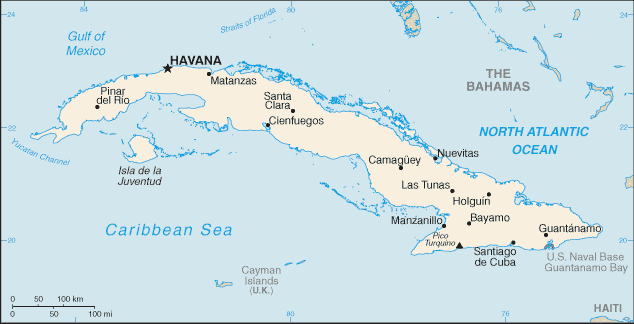 Introduction ::CubaBackground:The native Amerindian population of Cuba began to decline after the European discovery of the island by Christopher COLUMBUS in 1492 and following its development as a Spanish colony during the next several centuries. Large numbers of African slaves were imported to work the coffee and sugar plantations, and Havana became the launching point for the annual treasure fleets bound for Spain from Mexico and Peru. Spanish rule eventually provoked an independence movement and occasional rebellions that were harshly suppressed. US intervention during the Spanish-American War in 1898 assisted the Cubans in overthrowing Spanish rule. The Treaty of Paris established Cuban independence from the US in 1902 after which the island experienced a string of governments mostly dominated by the military and corrupt politicians. Fidel CASTRO led a rebel army to victory in 1959; his iron rule held the subsequent regime together for nearly five decades. He stepped down as president in February 2008 in favor of his younger brother Raul CASTRO. Cuba's communist revolution, with Soviet support, was exported throughout Latin America and Africa during the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s. The country faced a severe economic downturn in 1990 following the withdrawal of former Soviet subsidies worth $4 billion to $6 billion annually. Cuba at times portrays the US embargo, in place since 1961, as the source if its difficulties. Illicit migration to the US - using homemade rafts, alien smugglers, air flights, or via the US's southwest border - is a continuing problem. The US Coast Guard interdicted 1,275 Cuban nationals attempting to cross the Straits of Florida in 2012.Geography ::CubaLocation:Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, 150 km south of Key West, FloridaGeographic coordinates:21 30 N, 80 00 WArea:total: 110,860 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 106land: 109,820 sq kmwater: 1,040 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than PennsylvaniaLand boundaries:total: 29 kmborder countries: US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay 29 kmnote: Guantanamo Naval Base is leased by the US and remains part of CubaCoastline:3,735 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmClimate:tropical; moderated by trade winds; dry season (November to April); rainy season (May to October)Terrain:mostly flat to rolling plains, with rugged hills and mountains in the southeastElevation extremes:lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 mhighest point: Pico Turquino 2,005 mNatural resources:cobalt, nickel, iron ore, chromium, copper, salt, timber, silica, petroleum, arable landLand use:arable land: 32.31%permanent crops: 3.55%other: 64.15% (2011)Irrigated land:8,703 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:38.12 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 4.42 cu km/yr (22%/14%/65%)per capita: 392.6 cu m/yr (2010)Natural hazards:the east coast is subject to hurricanes from August to November (in general, the country averages about one hurricane every other year); droughts are commonEnvironment - current issues:air and water pollution; biodiversity loss; deforestationEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:largest country in Caribbean and westernmost island of the Greater AntillesPeople and Society ::CubaNationality:noun: Cuban(s)adjective: CubanEthnic groups:white 65.1%, mulatto and mestizo 24.8%, black 10.1% (2002 census)Languages:Spanish (official)Religions:nominally Roman Catholic 85%, Protestant, Jehovah's Witnesses, Jewish, Santerianote: prior to CASTRO assuming powerPopulation:11,061,886 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 77Age structure:0-14 years: 16.6% (male 944,254/female 892,766)15-24 years: 13.9% (male 787,368/female 748,315)25-54 years: 46.9% (male 2,611,371/female 2,578,471)55-64 years: 10.3% (male 544,465/female 595,856)65 years and over: 12.3% (male 611,086/female 747,934) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 41.9 %youth dependency ratio: 23 %elderly dependency ratio: 18.9 %potential support ratio: 5.3 (2013)Median age:total: 39.5 yearsmale: 38.6 yearsfemale: 40.3 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:-0.13% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 209Birth rate:9.92 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 197Death rate:7.58 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 114Net migration rate:-3.61 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 186Urbanization:urban population: 75% of total population (2010)rate of urbanization: 0% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:HAVANA (capital) 2.116 million (2011)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.01 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.91 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.82 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Maternal mortality rate:73 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 86Infant mortality rate:total: 4.76 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 183male: 5.12 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 4.39 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 78.05 yearscountry comparison to the world: 59male: 75.77 yearsfemale: 80.46 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.46 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 196Contraceptive prevalence rate:74.3% (2011)Health expenditures:10.6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 24Physicians density:6.4 physicians/1,000 population (2007)Hospital bed density:5.9 beds/1,000 population (2010)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 96% of populationrural: 89% of populationtotal: 94% of populationunimproved:urban: 4% of populationrural: 11% of populationtotal: 6% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 94% of populationrural: 81% of populationtotal: 91% of populationunimproved:urban: 6% of populationrural: 19% of populationtotal: 9% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 119HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:7,100 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 111HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 100 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 148Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: intermediatefood or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis Avectorborne diseases: dengue fever (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:21.5% (2008)country comparison to the world: 85Children under the age of 5 years underweight:3.4% (2000)country comparison to the world: 105Education expenditures:12.9% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 2Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99.8%male: 99.8%female: 99.8% (2011 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 15 yearsmale: 15 yearsfemale: 16 years (2011)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 3.1%country comparison to the world: 139male: 2.8%female: 3.5% (2008)People - note:illicit emigration is a continuing problem; Cubans attempt to depart the island and enter the US using homemade rafts, alien smugglers, direct flights, or falsified visas; Cubans also use non-maritime routes to enter the US including direct flights to Miami and over-land via the southwest borderGovernment ::CubaCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Cubaconventional short form: Cubalocal long form: Republica de Cubalocal short form: CubaGovernment type:Communist stateCapital:name: Havanageographic coordinates: 23 07 N, 82 21 Wtime difference: UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in March; ends first Sunday in November; note - Cuba has been known to alter the schedule of DST on short notice in an attempt to conserve electricity for lightingAdministrative divisions:15 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia) and 1 special municipality* (municipio especial); Artemisa, Camaguey, Ciego de Avila, Cienfuegos, Granma, Guantanamo, Holguin, Isla de la Juventud*, La Habana, Las Tunas, Matanzas, Mayabeque, Pinar del Rio, Sancti Spiritus, Santiago de Cuba, Villa ClaraIndependence:20 May 1902 (from Spain 10 December 1898; administered by the US from 1898 to 1902); not acknowledged by the Cuban Government as a day of independenceNational holiday:Triumph of the Revolution, 1 January (1959)Constitution:24 February 1976; amended July 1992 and June 2002Legal system:civil law system based on Spanish civil codeInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:16 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President of the Council of State and President of the Council of Ministers Gen. Raul CASTRO Ruz (president since 24 February 2008); First Vice President of the Council of State and First Vice President of the Council of Ministers Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez (since 24 February 2013); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President of the Council of State and President of the Council of Ministers Gen. Raul CASTRO Ruz (president since 24 February 2008); First Vice President of the Council of State and First Vice President of the Council of Ministers Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez (since 24 February 2013)cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the president of the Council of State and appointed by the National Assembly or the 28-member Council of State, elected by the assembly to act on its behalf when it is not in session(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president and vice presidents elected by the National Assembly for a five-year term; election last held on 24 February 2013 (next to be held in 2018)election results: Gen. Raul CASTRO Ruz reelected president; percent of legislative vote - 100%; Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez elected vice president; percent of legislative vote - 100%Legislative branch:unicameral National Assembly of People's Power or Asemblea Nacional del Poder Popular (number of seats in the National Assembly is based on population; 614 seats; members elected directly from slates approved by special candidacy commissions to serve five-year terms)elections: last held on 3 February 2013 (next to be held in 2018)election results: Cuba's Communist Party is the only legal party, and officially sanctioned candidates run unopposedJudicial branch:highest court(s): People's Supreme Court (consists of court president, vice president, 41 professional justices, and NA lay judges; organized into the ""Whole,"" State Council, and criminal, civil, administrative, labor, crimes against the state, and military courts)judge selection and term of office: professional judges elected by the National Assembly to serve 2.5-year terms; lay judges nominated by workplace collectives and neighborhood associations and elected by municipal or provincial assemblies; lay judges appointed for 5-year terms and serve up to 30 days per yearsubordinate courts: People's Provincial Courts; People's Regional Courts; People's CourtsPolitical parties and leaders:Cuban Communist Party or PCC [Raul CASTRO Ruz, first secretary]Political pressure groups and leaders:Human Rights WatchNational Association of Small FarmersInternational organization participation:ACP, ALBA, AOSIS, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IAEA, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IFAD, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, NAM, OAS (excluded from formal participation since 1962), OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:none; note - Cuba has an Interests Section in the Swiss Embassy, headed by Principal Officer Jorge BOLANOS Suarez; address: Cuban Interests Section, Swiss Embassy, 2630 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009; telephone: [1] (202) 797-8518; FAX: [1] (202) 797-8521Diplomatic representation from the US:none; note - the US has an Interests Section in the Swiss Embassy, headed by Chief of Mission John P. CAULFIELD; address: USINT, Swiss Embassy, Calzada between L and M Streets, Vedado, Havana; telephone: [53] (7) 839-4100; FAX: [53] (7) 839-4247; protecting power in Cuba is SwitzerlandFlag description:five equal horizontal bands of blue (top, center, and bottom) alternating with white; a red equilateral triangle based on the hoist side bears a white, five-pointed star in the center; the blue bands refer to the three old divisions of the island: central, occidental, and oriental; the white bands describe the purity of the independence ideal; the triangle symbolizes liberty, equality, and fraternity, while the red color stands for the blood shed in the independence struggle; the white star, called La Estrella Solitaria (the Lone Star) lights the way to freedom and was taken from the flag of Texasnote: design similar to the Puerto Rican flag, with the colors of the bands and triangle reversedNational anthem:name: ""La Bayamesa"" (The Bayamo Song)lyrics/music: Pedro FIGUEREDOnote: adopted 1940; Pedro FIGUEREDO first performed ""La Bayamesa"" in 1868 during the Ten Years War against the Spanish; a leading figure in the uprising, FIGUEREDO was captured in 1870 and executed by a firing squad; just prior to the fusillade he is reputed to have shouted, ""Morir por la Patria es vivir"" (To die for the country is to live), a line from the anthemEconomy ::CubaEconomy - overview:The government continues to balance the need for loosening its socialist economic system against a desire for firm political control. The government in April 2011 held the first Cuban Communist Party Congress in almost 13 years, during which leaders approved a plan for wide-ranging economic changes. President Raul CASTRO said such changes were needed to update the economic model to ensure the survival of socialism. The government has expanded opportunities for self-employment and has introduced limited reforms, some initially implemented in the 1990s, to increase enterprise efficiency and alleviate serious shortages of food, consumer goods, services, and housing. The average Cuban's standard of living remains at a lower level than before the downturn of the 1990s, which was caused by the loss of Soviet aid and domestic inefficiencies. Since late 2000, Venezuela has been providing oil on preferential terms, and it currently supplies over 100,000 barrels per day of petroleum products. Cuba has been paying for the oil, in part, with the services of Cuban personnel in Venezuela including some 30,000 medical professionals.GDP (purchasing power parity):$121 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 68$117.3 billion (2011 est.)$114.1 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$72.3 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:3.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1052.8% (2011 est.)2.4% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$10,200 (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 117$10,000 (2009 est.)$10,000 (2008 est.)note: data are in 2010 US dollarsGross national saving:11.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 12111.7% of GDP (2011 est.)14.9% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 53.5%government consumption: 35.4%investment in fixed capital: 9.6%investment in inventories: -2.2%exports of goods and services: 24.6%imports of goods and services: -20.9%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 3.8%industry: 22.2%services: 74% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:sugar, tobacco, citrus, coffee, rice, potatoes, beans; livestockIndustries:petroleum, nickel/cobalt, pharmaceuticals, tobacco, construction, steel, cement, agricultural machinery, sugarIndustrial production growth rate:6.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Labor force:5.18 millioncountry comparison to the world: 74note: state sector 72.3%, non-state sector 27.7% (2012 est.)Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 19.7%industry: 17.1%services: 63.2% (2011)Unemployment rate:3.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 293.2% (2011 est.)note: these are official rates; unofficial estimates are about double the official figuresPopulation below poverty line:NA%Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: NA%highest 10%: NA%Budget:revenues: $47.78 billionexpenditures: $50.45 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:66.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 6Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-3.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 134Public debt:35.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 10336% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):5.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1544.8% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:NA%Commercial bank prime lending rate:NA%Stock of narrow money:$10.97 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 75$10.65 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$36.29 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 74$34.77 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$NACurrent account balance:$1 billion (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 42$1.4 billion (2010 est.)Exports:$5.972 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 108$6.34 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:petroleum, nickel, medical products, sugar, tobacco, fish, citrus, coffeeExports - partners:Canada 17.3%, China 16.6%, Venezuela 12.7%, Netherlands 8.8%, Spain 5.8% (2012)Imports:$13.72 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 90$14.02 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:petroleum, food, machinery and equipment, chemicalsImports - partners:Venezuela 36.4%, China 10.5%, Spain 8.7%, Brazil 5.1%, US 4.2% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$4.693 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 95$4.393 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$22.51 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 79$21.88 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$NAStock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$4.138 billion (2006 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Exchange rates:Cuban pesos (CUP) per US dollar -1 (2012 est.)0.9847 (2011 est.)0.9259 (2010 est.)0.9259 (2009)0.9259 (2008)Energy ::CubaElectricity - production:17.8 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Electricity - consumption:16.38 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 73Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 182Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Electricity - installed generating capacity:5.914 million kW (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Electricity - from fossil fuels:99.3% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 56Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 143Electricity - from other renewable sources:0.1% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Crude oil - production:53,000 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Crude oil - exports:83,000 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 40Crude oil - imports:165,000 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Crude oil - proved reserves:181.5 million bbl (1 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Refined petroleum products - production:104,200 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 73Refined petroleum products - consumption:150,200 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 66Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 167Refined petroleum products - imports:73,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 55Natural gas - production:1.03 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Natural gas - consumption:1.03 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 89Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Natural gas - proved reserves:70.79 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 60Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:34.46 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 74Communications ::CubaTelephones - main lines in use:1.193 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 70Telephones - mobile cellular:1.315 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 149Telephone system:general assessment: greater investment beginning in 1994 and the establishment of a new Ministry of Information Technology and Communications in 2000 has resulted in improvements in the system; national fiber-optic system under development; 95% of switches digitized by end of 2006; mobile-cellular telephone service is expensive and must be paid in convertible pesos, which effectively limits subscribershipdomestic: fixed-line density remains low at 10 per 100 inhabitants; mobile-cellular service expanding but remains only about 10 per 100 personsinternational: country code - 53; fiber-optic cable laid to but not linked to US network; satellite earth station - 1 Intersputnik (Atlantic Ocean region) (2010)Broadcast media:government owns and controls all broadcast media with private ownership of electronic media prohibited; government operates 4 national TV networks and many local TV stations; government operates 6 national radio networks, an international station, and many local radio stations; Radio-TV Marti is beamed from the US (2007)Internet country code:.cuInternet hosts:3,244 (2012)country comparison to the world: 154Internet users:1.606 millioncountry comparison to the world: 79note: private citizens are prohibited from buying computers or accessing the Internet without special authorization; foreigners may access the Internet in large hotels but are subject to firewalls; some Cubans buy illegal passwords on the black market or take advantage of public outlets to access limited email and the government-controlled ""intranet"" (2009)Transportation ::CubaAirports:133 (2013)country comparison to the world: 42Airports - with paved runways:total: 64over 3,047 m: 72,438 to 3,047 m: 101,524 to 2,437 m: 16914 to 1,523 m: 4under 914 m: 27 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 69914 to 1,523 m: 11under 914 m:58 (2013)Pipelines:gas 41 km; oil 230 km (2013)Railways:total: 8,203 kmcountry comparison to the world: 25standard gauge: 8,134 km 1.435-m gauge (124 km electrified)narrow gauge: 69 km 1.000-m gaugenote: 48 km of standard gauge track is not for public use (2011)Roadways:total: 60,858 kmcountry comparison to the world: 72paved: 29,820 km (includes 639 km of expressways)unpaved: 31,038 km (2001)Waterways:240 km (almost all navigable inland waterways are near the mouths of rivers) (2011)country comparison to the world: 95Merchant marine:total: 3country comparison to the world: 136by type: cargo 1, passenger 1, refrigerated cargo 1registered in other countries: 5 (Curacao 1, Panama 2, unknown 2) (2010)Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Antilla, Cienfuegos, Guantanamo, Havana, Matanzas, Mariel, Nuevitas Bay, Santiago de CubaMilitary ::CubaMilitary branches:Revolutionary Armed Forces (Fuerzas Armadas Revolucionarias, FAR): Revolutionary Army (Ejercito Revolucionario, ER, includes Territorial Militia Troops (Milicia de Tropas de Territoriales, MTT)); Revolutionary Navy (Marina de Guerra Revolucionaria, MGR, includes Marine Corps); Revolutionary Air and Air Defense Forces (Defensas Anti-Aereas y Fuerza Aerea Revolucionaria, DAAFAR), Youth Labor Army (Ejercito Juvenil del Trabajo, EJT) (2011)Military service age and obligation:17-28 years of age for compulsory military service; 2-year service obligation; both sexes subject to military service (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 2,998,201females age 16-49: 2,919,107 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 2,446,131females age 16-49: 2,375,590 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 72,823female: 69,108 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:3.2% of GDP (2011)country comparison to the world: 37Military - note:the collapse of the Soviet Union deprived the Cuban military of its major economic and logistic support and had a significant impact on the state of Cuban equipment; the army remains well trained and professional in nature; while the lack of replacement parts for its existing equipment has increasingly affected operational capabilities, Cuba remains able to offer considerable resistance to any regional power (2010)Transnational Issues ::CubaDisputes - international:US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay is leased to US and only mutual agreement or US abandonment of the facility can terminate the leaseTrafficking in persons:current situation: Cuba is a source country for adults and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; child prostitution and child sex tourism reportedly occurs in Cuba, and laws do not appear to penalize the prostitution of children between the ages of 16 and 18; allegations have been made of Cubans being subjected to forced labor, particularly with Cuban work missions abroad; the scope of trafficking within Cuba is particularly difficult to gauge due to the closed nature of the government and sparse non-governmental or independent reportingtier rating: Tier 3 - Cuba does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; the government has not publicized information about government measures to address human trafficking through prosecution, protection, or prevention efforts but did share information about its general approach to protection for children and youth; the government has a network of shelters for victims of domestic violence and child abuse but has not verified if trafficking victims receive care in those centers (2013)Illicit drugs:territorial waters and air space serve as transshipment zone for US- and European-bound drugs; established the death penalty for certain drug-related crimes in 1999 (2008)"
Introduction ::CubaBackground:The native Amerindian population of Cuba began to decline after the European discovery of the island by Christopher COLUMBUS in 1492 and following its development as a Spanish colony during the next several centuries. Large numbers of African slaves were imported to work the coffee and sugar plantations, and Havana became the launching point for the annual treasure fleets bound for Spain from Mexico and Peru. Spanish rule eventually provoked an independence movement and occasional rebellions that were harshly suppressed. US intervention during the Spanish-American War in 1898 assisted the Cubans in overthrowing Spanish rule. The Treaty of Paris established Cuban independence from the US in 1902 after which the island experienced a string of governments mostly dominated by the military and corrupt politicians. Fidel CASTRO led a rebel army to victory in 1959; his iron rule held the subsequent regime together for nearly five decades. He stepped down as president in February 2008 in favor of his younger brother Raul CASTRO. Cuba's communist revolution, with Soviet support, was exported throughout Latin America and Africa during the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s. The country faced a severe economic downturn in 1990 following the withdrawal of former Soviet subsidies worth $4 billion to $6 billion annually. Cuba at times portrays the US embargo, in place since 1961, as the source if its difficulties. Illicit migration to the US - using homemade rafts, alien smugglers, air flights, or via the US's southwest border - is a continuing problem. The US Coast Guard interdicted 1,275 Cuban nationals attempting to cross the Straits of Florida in 2012.Geography ::CubaLocation:Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, 150 km south of Key West, FloridaGeographic coordinates:21 30 N, 80 00 WArea:total: 110,860 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 106land: 109,820 sq kmwater: 1,040 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than PennsylvaniaLand boundaries:total: 29 kmborder countries: US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay 29 kmnote: Guantanamo Naval Base is leased by the US and remains part of CubaCoastline:3,735 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmClimate:tropical; moderated by trade winds; dry season (November to April); rainy season (May to October)Terrain:mostly flat to rolling plains, with rugged hills and mountains in the southeastElevation extremes:lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 mhighest point: Pico Turquino 2,005 mNatural resources:cobalt, nickel, iron ore, chromium, copper, salt, timber, silica, petroleum, arable landLand use:arable land: 32.31%permanent crops: 3.55%other: 64.15% (2011)Irrigated land:8,703 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:38.12 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 4.42 cu km/yr (22%/14%/65%)per capita: 392.6 cu m/yr (2010)Natural hazards:the east coast is subject to hurricanes from August to November (in general, the country averages about one hurricane every other year); droughts are commonEnvironment - current issues:air and water pollution; biodiversity loss; deforestationEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:largest country in Caribbean and westernmost island of the Greater AntillesPeople and Society ::CubaNationality:noun: Cuban(s)adjective: CubanEthnic groups:white 65.1%, mulatto and mestizo 24.8%, black 10.1% (2002 census)Languages:Spanish (official)Religions:nominally Roman Catholic 85%, Protestant, Jehovah's Witnesses, Jewish, Santerianote: prior to CASTRO assuming powerPopulation:11,061,886 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 77Age structure:0-14 years: 16.6% (male 944,254/female 892,766)15-24 years: 13.9% (male 787,368/female 748,315)25-54 years: 46.9% (male 2,611,371/female 2,578,471)55-64 years: 10.3% (male 544,465/female 595,856)65 years and over: 12.3% (male 611,086/female 747,934) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 41.9 %youth dependency ratio: 23 %elderly dependency ratio: 18.9 %potential support ratio: 5.3 (2013)Median age:total: 39.5 yearsmale: 38.6 yearsfemale: 40.3 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:-0.13% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 209Birth rate:9.92 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 197Death rate:7.58 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 114Net migration rate:-3.61 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 186Urbanization:urban population: 75% of total population (2010)rate of urbanization: 0% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:HAVANA (capital) 2.116 million (2011)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.01 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.91 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.82 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Maternal mortality rate:73 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 86Infant mortality rate:total: 4.76 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 183male: 5.12 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 4.39 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 78.05 yearscountry comparison to the world: 59male: 75.77 yearsfemale: 80.46 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.46 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 196Contraceptive prevalence rate:74.3% (2011)Health expenditures:10.6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 24Physicians density:6.4 physicians/1,000 population (2007)Hospital bed density:5.9 beds/1,000 population (2010)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 96% of populationrural: 89% of populationtotal: 94% of populationunimproved:urban: 4% of populationrural: 11% of populationtotal: 6% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 94% of populationrural: 81% of populationtotal: 91% of populationunimproved:urban: 6% of populationrural: 19% of populationtotal: 9% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 119HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:7,100 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 111HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 100 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 148Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: intermediatefood or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis Avectorborne diseases: dengue fever (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:21.5% (2008)country comparison to the world: 85Children under the age of 5 years underweight:3.4% (2000)country comparison to the world: 105Education expenditures:12.9% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 2Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99.8%male: 99.8%female: 99.8% (2011 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 15 yearsmale: 15 yearsfemale: 16 years (2011)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 3.1%country comparison to the world: 139male: 2.8%female: 3.5% (2008)People - note:illicit emigration is a continuing problem; Cubans attempt to depart the island and enter the US using homemade rafts, alien smugglers, direct flights, or falsified visas; Cubans also use non-maritime routes to enter the US including direct flights to Miami and over-land via the southwest borderGovernment ::CubaCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Cubaconventional short form: Cubalocal long form: Republica de Cubalocal short form: CubaGovernment type:Communist stateCapital:name: Havanageographic coordinates: 23 07 N, 82 21 Wtime difference: UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in March; ends first Sunday in November; note - Cuba has been known to alter the schedule of DST on short notice in an attempt to conserve electricity for lightingAdministrative divisions:15 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia) and 1 special municipality* (municipio especial); Artemisa, Camaguey, Ciego de Avila, Cienfuegos, Granma, Guantanamo, Holguin, Isla de la Juventud*, La Habana, Las Tunas, Matanzas, Mayabeque, Pinar del Rio, Sancti Spiritus, Santiago de Cuba, Villa ClaraIndependence:20 May 1902 (from Spain 10 December 1898; administered by the US from 1898 to 1902); not acknowledged by the Cuban Government as a day of independenceNational holiday:Triumph of the Revolution, 1 January (1959)Constitution:24 February 1976; amended July 1992 and June 2002Legal system:civil law system based on Spanish civil codeInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:16 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President of the Council of State and President of the Council of Ministers Gen. Raul CASTRO Ruz (president since 24 February 2008); First Vice President of the Council of State and First Vice President of the Council of Ministers Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez (since 24 February 2013); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President of the Council of State and President of the Council of Ministers Gen. Raul CASTRO Ruz (president since 24 February 2008); First Vice President of the Council of State and First Vice President of the Council of Ministers Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez (since 24 February 2013)cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the president of the Council of State and appointed by the National Assembly or the 28-member Council of State, elected by the assembly to act on its behalf when it is not in session(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president and vice presidents elected by the National Assembly for a five-year term; election last held on 24 February 2013 (next to be held in 2018)election results: Gen. Raul CASTRO Ruz reelected president; percent of legislative vote - 100%; Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez elected vice president; percent of legislative vote - 100%Legislative branch:unicameral National Assembly of People's Power or Asemblea Nacional del Poder Popular (number of seats in the National Assembly is based on population; 614 seats; members elected directly from slates approved by special candidacy commissions to serve five-year terms)elections: last held on 3 February 2013 (next to be held in 2018)election results: Cuba's Communist Party is the only legal party, and officially sanctioned candidates run unopposedJudicial branch:highest court(s): People's Supreme Court (consists of court president, vice president, 41 professional justices, and NA lay judges; organized into the ""Whole,"" State Council, and criminal, civil, administrative, labor, crimes against the state, and military courts)judge selection and term of office: professional judges elected by the National Assembly to serve 2.5-year terms; lay judges nominated by workplace collectives and neighborhood associations and elected by municipal or provincial assemblies; lay judges appointed for 5-year terms and serve up to 30 days per yearsubordinate courts: People's Provincial Courts; People's Regional Courts; People's CourtsPolitical parties and leaders:Cuban Communist Party or PCC [Raul CASTRO Ruz, first secretary]Political pressure groups and leaders:Human Rights WatchNational Association of Small FarmersInternational organization participation:ACP, ALBA, AOSIS, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IAEA, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IFAD, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, NAM, OAS (excluded from formal participation since 1962), OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:none; note - Cuba has an Interests Section in the Swiss Embassy, headed by Principal Officer Jorge BOLANOS Suarez; address: Cuban Interests Section, Swiss Embassy, 2630 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009; telephone: [1] (202) 797-8518; FAX: [1] (202) 797-8521Diplomatic representation from the US:none; note - the US has an Interests Section in the Swiss Embassy, headed by Chief of Mission John P. CAULFIELD; address: USINT, Swiss Embassy, Calzada between L and M Streets, Vedado, Havana; telephone: [53] (7) 839-4100; FAX: [53] (7) 839-4247; protecting power in Cuba is SwitzerlandFlag description:five equal horizontal bands of blue (top, center, and bottom) alternating with white; a red equilateral triangle based on the hoist side bears a white, five-pointed star in the center; the blue bands refer to the three old divisions of the island: central, occidental, and oriental; the white bands describe the purity of the independence ideal; the triangle symbolizes liberty, equality, and fraternity, while the red color stands for the blood shed in the independence struggle; the white star, called La Estrella Solitaria (the Lone Star) lights the way to freedom and was taken from the flag of Texasnote: design similar to the Puerto Rican flag, with the colors of the bands and triangle reversedNational anthem:name: ""La Bayamesa"" (The Bayamo Song)lyrics/music: Pedro FIGUEREDOnote: adopted 1940; Pedro FIGUEREDO first performed ""La Bayamesa"" in 1868 during the Ten Years War against the Spanish; a leading figure in the uprising, FIGUEREDO was captured in 1870 and executed by a firing squad; just prior to the fusillade he is reputed to have shouted, ""Morir por la Patria es vivir"" (To die for the country is to live), a line from the anthemEconomy ::CubaEconomy - overview:The government continues to balance the need for loosening its socialist economic system against a desire for firm political control. The government in April 2011 held the first Cuban Communist Party Congress in almost 13 years, during which leaders approved a plan for wide-ranging economic changes. President Raul CASTRO said such changes were needed to update the economic model to ensure the survival of socialism. The government has expanded opportunities for self-employment and has introduced limited reforms, some initially implemented in the 1990s, to increase enterprise efficiency and alleviate serious shortages of food, consumer goods, services, and housing. The average Cuban's standard of living remains at a lower level than before the downturn of the 1990s, which was caused by the loss of Soviet aid and domestic inefficiencies. Since late 2000, Venezuela has been providing oil on preferential terms, and it currently supplies over 100,000 barrels per day of petroleum products. Cuba has been paying for the oil, in part, with the services of Cuban personnel in Venezuela including some 30,000 medical professionals.GDP (purchasing power parity):$121 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 68$117.3 billion (2011 est.)$114.1 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$72.3 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:3.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1052.8% (2011 est.)2.4% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$10,200 (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 117$10,000 (2009 est.)$10,000 (2008 est.)note: data are in 2010 US dollarsGross national saving:11.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 12111.7% of GDP (2011 est.)14.9% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 53.5%government consumption: 35.4%investment in fixed capital: 9.6%investment in inventories: -2.2%exports of goods and services: 24.6%imports of goods and services: -20.9%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 3.8%industry: 22.2%services: 74% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:sugar, tobacco, citrus, coffee, rice, potatoes, beans; livestockIndustries:petroleum, nickel/cobalt, pharmaceuticals, tobacco, construction, steel, cement, agricultural machinery, sugarIndustrial production growth rate:6.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Labor force:5.18 millioncountry comparison to the world: 74note: state sector 72.3%, non-state sector 27.7% (2012 est.)Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 19.7%industry: 17.1%services: 63.2% (2011)Unemployment rate:3.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 293.2% (2011 est.)note: these are official rates; unofficial estimates are about double the official figuresPopulation below poverty line:NA%Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: NA%highest 10%: NA%Budget:revenues: $47.78 billionexpenditures: $50.45 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:66.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 6Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-3.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 134Public debt:35.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 10336% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):5.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1544.8% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:NA%Commercial bank prime lending rate:NA%Stock of narrow money:$10.97 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 75$10.65 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$36.29 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 74$34.77 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$NACurrent account balance:$1 billion (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 42$1.4 billion (2010 est.)Exports:$5.972 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 108$6.34 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:petroleum, nickel, medical products, sugar, tobacco, fish, citrus, coffeeExports - partners:Canada 17.3%, China 16.6%, Venezuela 12.7%, Netherlands 8.8%, Spain 5.8% (2012)Imports:$13.72 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 90$14.02 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:petroleum, food, machinery and equipment, chemicalsImports - partners:Venezuela 36.4%, China 10.5%, Spain 8.7%, Brazil 5.1%, US 4.2% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$4.693 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 95$4.393 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$22.51 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 79$21.88 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$NAStock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$4.138 billion (2006 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Exchange rates:Cuban pesos (CUP) per US dollar -1 (2012 est.)0.9847 (2011 est.)0.9259 (2010 est.)0.9259 (2009)0.9259 (2008)Energy ::CubaElectricity - production:17.8 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Electricity - consumption:16.38 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 73Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 182Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Electricity - installed generating capacity:5.914 million kW (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Electricity - from fossil fuels:99.3% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 56Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 143Electricity - from other renewable sources:0.1% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Crude oil - production:53,000 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Crude oil - exports:83,000 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 40Crude oil - imports:165,000 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Crude oil - proved reserves:181.5 million bbl (1 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Refined petroleum products - production:104,200 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 73Refined petroleum products - consumption:150,200 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 66Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 167Refined petroleum products - imports:73,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 55Natural gas - production:1.03 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Natural gas - consumption:1.03 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 89Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Natural gas - proved reserves:70.79 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 60Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:34.46 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 74Communications ::CubaTelephones - main lines in use:1.193 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 70Telephones - mobile cellular:1.315 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 149Telephone system:general assessment: greater investment beginning in 1994 and the establishment of a new Ministry of Information Technology and Communications in 2000 has resulted in improvements in the system; national fiber-optic system under development; 95% of switches digitized by end of 2006; mobile-cellular telephone service is expensive and must be paid in convertible pesos, which effectively limits subscribershipdomestic: fixed-line density remains low at 10 per 100 inhabitants; mobile-cellular service expanding but remains only about 10 per 100 personsinternational: country code - 53; fiber-optic cable laid to but not linked to US network; satellite earth station - 1 Intersputnik (Atlantic Ocean region) (2010)Broadcast media:government owns and controls all broadcast media with private ownership of electronic media prohibited; government operates 4 national TV networks and many local TV stations; government operates 6 national radio networks, an international station, and many local radio stations; Radio-TV Marti is beamed from the US (2007)Internet country code:.cuInternet hosts:3,244 (2012)country comparison to the world: 154Internet users:1.606 millioncountry comparison to the world: 79note: private citizens are prohibited from buying computers or accessing the Internet without special authorization; foreigners may access the Internet in large hotels but are subject to firewalls; some Cubans buy illegal passwords on the black market or take advantage of public outlets to access limited email and the government-controlled ""intranet"" (2009)Transportation ::CubaAirports:133 (2013)country comparison to the world: 42Airports - with paved runways:total: 64over 3,047 m: 72,438 to 3,047 m: 101,524 to 2,437 m: 16914 to 1,523 m: 4under 914 m: 27 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 69914 to 1,523 m: 11under 914 m:58 (2013)Pipelines:gas 41 km; oil 230 km (2013)Railways:total: 8,203 kmcountry comparison to the world: 25standard gauge: 8,134 km 1.435-m gauge (124 km electrified)narrow gauge: 69 km 1.000-m gaugenote: 48 km of standard gauge track is not for public use (2011)Roadways:total: 60,858 kmcountry comparison to the world: 72paved: 29,820 km (includes 639 km of expressways)unpaved: 31,038 km (2001)Waterways:240 km (almost all navigable inland waterways are near the mouths of rivers) (2011)country comparison to the world: 95Merchant marine:total: 3country comparison to the world: 136by type: cargo 1, passenger 1, refrigerated cargo 1registered in other countries: 5 (Curacao 1, Panama 2, unknown 2) (2010)Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Antilla, Cienfuegos, Guantanamo, Havana, Matanzas, Mariel, Nuevitas Bay, Santiago de CubaMilitary ::CubaMilitary branches:Revolutionary Armed Forces (Fuerzas Armadas Revolucionarias, FAR): Revolutionary Army (Ejercito Revolucionario, ER, includes Territorial Militia Troops (Milicia de Tropas de Territoriales, MTT)); Revolutionary Navy (Marina de Guerra Revolucionaria, MGR, includes Marine Corps); Revolutionary Air and Air Defense Forces (Defensas Anti-Aereas y Fuerza Aerea Revolucionaria, DAAFAR), Youth Labor Army (Ejercito Juvenil del Trabajo, EJT) (2011)Military service age and obligation:17-28 years of age for compulsory military service; 2-year service obligation; both sexes subject to military service (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 2,998,201females age 16-49: 2,919,107 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 2,446,131females age 16-49: 2,375,590 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 72,823female: 69,108 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:3.2% of GDP (2011)country comparison to the world: 37Military - note:the collapse of the Soviet Union deprived the Cuban military of its major economic and logistic support and had a significant impact on the state of Cuban equipment; the army remains well trained and professional in nature; while the lack of replacement parts for its existing equipment has increasingly affected operational capabilities, Cuba remains able to offer considerable resistance to any regional power (2010)Transnational Issues ::CubaDisputes - international:US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay is leased to US and only mutual agreement or US abandonment of the facility can terminate the leaseTrafficking in persons:current situation: Cuba is a source country for adults and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; child prostitution and child sex tourism reportedly occurs in Cuba, and laws do not appear to penalize the prostitution of children between the ages of 16 and 18; allegations have been made of Cubans being subjected to forced labor, particularly with Cuban work missions abroad; the scope of trafficking within Cuba is particularly difficult to gauge due to the closed nature of the government and sparse non-governmental or independent reportingtier rating: Tier 3 - Cuba does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; the government has not publicized information about government measures to address human trafficking through prosecution, protection, or prevention efforts but did share information about its general approach to protection for children and youth; the government has a network of shelters for victims of domestic violence and child abuse but has not verified if trafficking victims receive care in those centers (2013)Illicit drugs:territorial waters and air space serve as transshipment zone for US- and European-bound drugs; established the death penalty for certain drug-related crimes in 1999 (2008)"
The World Factbook. 2014.
